Diving into the differences between agentic AI and generative AI means first defining both.
Generative AI
Generative AI is artificial intelligence that can create original content such as text, images, video, audio or software code in response to a user’s prompt or request. Gen AI relies on using machine learning models called deep learning models algorithms that simulate the learning and decision-making processes of the human brain and other technologies like robotic process automation (RPA).
These models work by identifying and encoding the patterns and relationships in huge amounts of data, and then using that information to understand users' natural language requests or questions. These models can then generate high-quality text, images, and other content based on the data they were trained on in real-time.
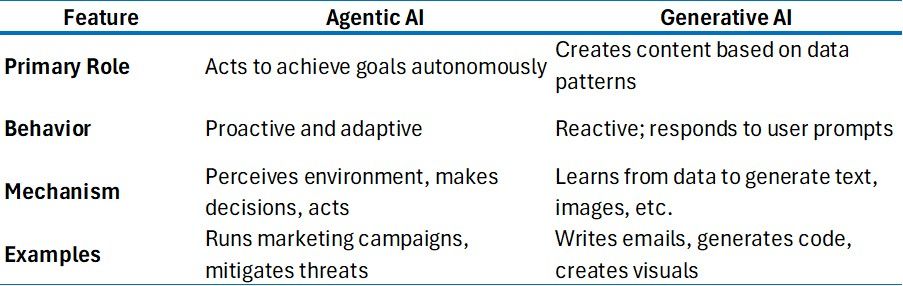
- Focus: Content creation.
- Mechanism: Learns patterns from large datasets to generate new, original content like text, images, audio, and video.
- Behavior: Reactive; it needs a user prompt to initiate its action.
- Example: Creating marketing content, drafting emails, or generating code.
Agentic AI
Agentic AI describes AI systems that are designed to autonomously make decisions and act, with the ability to pursue complex goals with limited supervision. It brings together the flexible characteristics of large language models (LLMs) with the accuracy of traditional programming. This type of AI acts autonomously to achieve a goal by using technologies like natural language processing (NLPs), machine learning, reinforcement learning and knowledge representation. It’s a proactive AI-powered approach, whereas gen AI is reactive to the users input. Agentic AI can adapt to different or changing situations and has “agency” to make decisions based on context. It is used in various applications that can benefit from independent operation, such as robotics, complex analysis, and virtual assistants.
- Focus: Autonomous action and goal achievement.
- Mechanism: Perceives its environment, makes dynamic decisions, and executes a series of actions to reach specific, self-defined or given objectives.
- Behavior: Proactive and autonomous; it can adapt its plans in response to changing information or conditions without constant human oversight.
- Example: An agent launching and monitoring a marketing campaign by analyzing performance data and adjusting the strategy, or a system that analyzes security threats and autonomously mitigates them.
Key Differences Summarized.
Agentic AI and generative AI trends
Generative AI trends
- Gen AI augmented applications: There is a shift toward gen AI augmented applications being integrated into various software and platforms. This integration is helping make the user experience even more personal and provide intelligent functions.
- Synthetic data for model training: Synthetic data that is generated by AI will be used to train models where real-world data is not readily available or expensive. The use of synthetic data can improve AI training across industries like robotics, autonomous driving, and finance.
- Deepfake technology: While mildly entertaining, gen AI has invented a hyper-realistic image or video by using AI that appears real. It has and is raising ethical concerns surrounding misinformation.
- Content personalization: A popular trend is personalization when it come to retail. Marketing teams are adapting content and campaigns to individual preferences based on gen AI data analytics.
Agentic AI trends
- Financial services industry: Agentic AI has the potential to revolutionize trading strategies by analyzing market data and expediting executing trades. The extended reach of agentic AI is a significant benefit as agentic AI can be designed to search the web extensively. Agents are able to retrieve updates and obtain real-time information.
- Robotics: Places like Amazon warehouses have started to employ robots in fulfillment centers to streamline warehouse automation and manufacturing processes. Agentic AI can handle complex tasks and operate independently to perform specific tasks.
- City planning: Agentic AI systems in urban planning can analyze all types of datasets to help planners make informed decisions, such as real-time traffic data and camera sensors. The intuitive nature of agentic AI has the potential to alleviate teams of hours of work to create presentation slides or tables.
- Human resources: Agentic AI used for human resources can help organizations go beyond gen AI capabilities and instead provide autonomous decision-making and dynamic employee support. AI agents can automate routine work and provide personalized responses to employees, giving HR professionals time to deal with more strategic priorities.