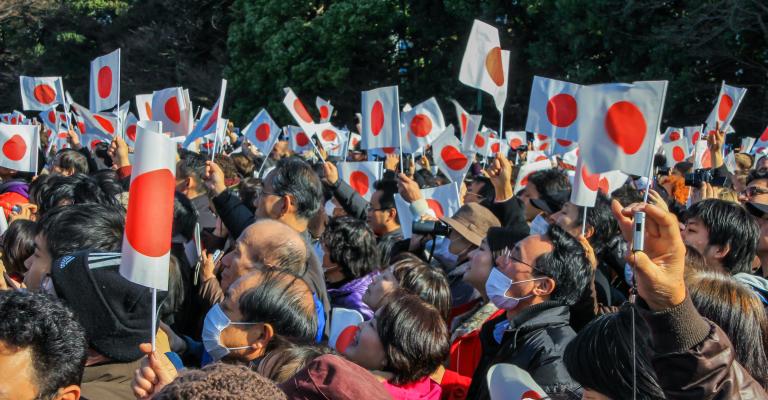
Japan's governing coalition loses upper house election on 20 July 2025.
Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba’s ruling coalition, made up of the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) and Komeito, suffered a major setback. They won only around 41 seats, falling short of the 50 needed to maintain control of the 248-seat chamber2. This marks the first time since 1955 that the LDP will govern without a majority in either house of parliament.
Othe other hand, Including Japan’s response to Trump-era tariffs, the political environment surrounding the country will continue to be significantly affected by global supply chain disruptions and the need for restructuring.
The Japanese government is actively pursuing strategies to enhance supply chain resilience, reduce reliance on specific countries, and promote domestic and Southeast Asian production. This includes significant investments in strategic industries like semiconductors and a focus on strengthening alliances with like-minded nations.
Key Impacts and Responses:
Reshoring and Diversification: Japan is actively encouraging the relocation of production back to Japan (onshoring) and diversifying supply chains beyond China.
Strategic Industries: The government is heavily subsidizing key industries like semiconductors to reduce reliance on foreign suppliers and enhance national security.
Geopolitical Considerations: The US-China rivalry and the potential for trade tensions are prompting Japan to reassess its supply chain dependencies and strengthen ties with countries like the US and those in Southeast Asia.
Economic Security: Japan's "Economic Security Promotion Act" mandates government actions to secure supply chains of critical materials and maintain the stability of key infrastructure.
Government Support: The Japanese government is providing financial assistance, tax incentives, and other support to companies investing in technology and sustainability, encouraging them to build more resilient supply chains.
Regional Partnerships: Japan is actively strengthening partnerships with Southeast Asian nations to diversify its production base and reduce its reliance on China.
Specific Examples:
Semiconductors: The Japanese government is heavily investing in domestic semiconductor manufacturing, including attracting Taiwanese chipmaker TSMC to build a plant in Japan.
Toyota: Toyota, a major Japanese automaker, has been significantly impacted by supply chain disruptions, leading to production suspensions and prompting the company to strengthen its supply network.
“China Plus One" Strategy: Japan's "China Plus One" strategy, which encourages companies to diversify their production bases, is gaining renewed attention due to recent global events.
In essence, Japan is actively reshaping its global supply chains to enhance economic security, reduce vulnerabilities, and strengthen its position in the global landscape.